Proposed Pipeline

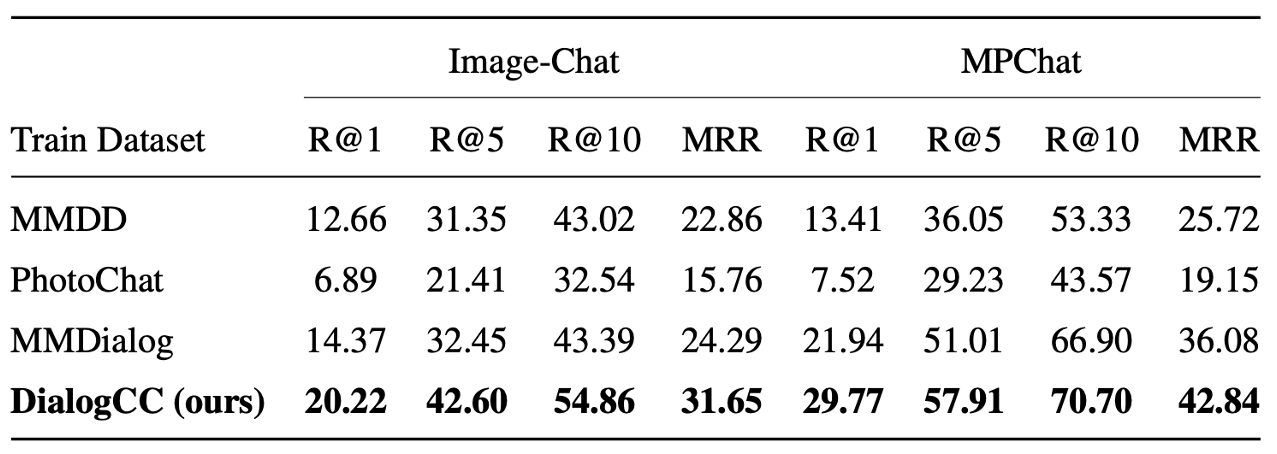
In order to construct DialogCC, we introduce an automatic pipeline, which consists of three steps: (1) collecting, (2) aligning, and (3) filtering.
- Collecting: We collect five multi-turn text-only social dialogue datasets (i.e., Persona-Chat, EmpatheticDialogues, Wizard-of-Wikipedia, DailyDialog, BlendedSkillTalk) and Conceptual Captions 3M (CC3M).
- Aligning: After collecting source datasets, to ensure image-dialogue coherence, we ask GPT-4 to infer all possible image-sharing moments via zero-shot prompting and leverage the CLIP to increase the aligned image relevancy.
- Filtering: We eliminate inappropriate images based on CLIP similarity for image-image consistency.